
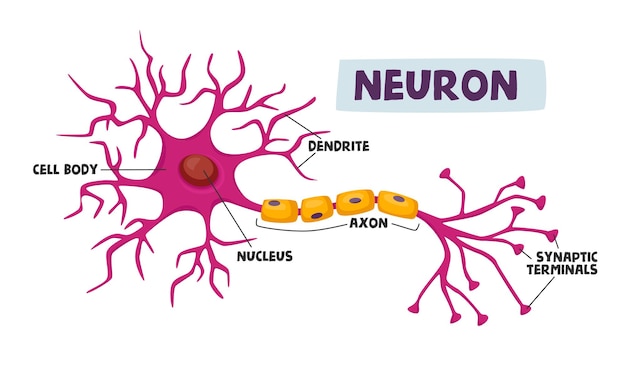
In sensory neurons, the dendrites are generally very long. The conference will be of interest to researchers and students in neuroscience, as well as to anyone interested in normal and abnormal brain function. Dendrites provide an enlarged surface area to receive signals from the terminal buttons of other axons, and the axon also commonly divides at its far end into many branches ( telodendria) each of which ends in a nerve terminal, allowing a chemical signal to pass simultaneously to many target cells. The dendrites branch-like projections that receive the signal. The dendrites branch-like projections that receive the signal. Dendrites receive electrical messages from the axons of neurons. These small structures are found at the end of neurons next to the axon. This Gordon Research Conference will bring together researchers whose latest findings help clarify how the properties of dendrites enable them to perform complex computations important for sensory-motor processing and higher cognitive function. Dendrites are tree-like structures that extend away from the cell body to receive messages from other neurons at specialized junctions called synapses. What Is the Function of Dendrites By Staff Writer Last Updated MaDendrites receive information from neurons in the form of action potentials. Computational and theoretical approaches have further refined our views of dendrites and their unique role in brain function. Neurons are large, tree-like structures made up of a body, the soma, with numerous branches called dendrites extending outward.
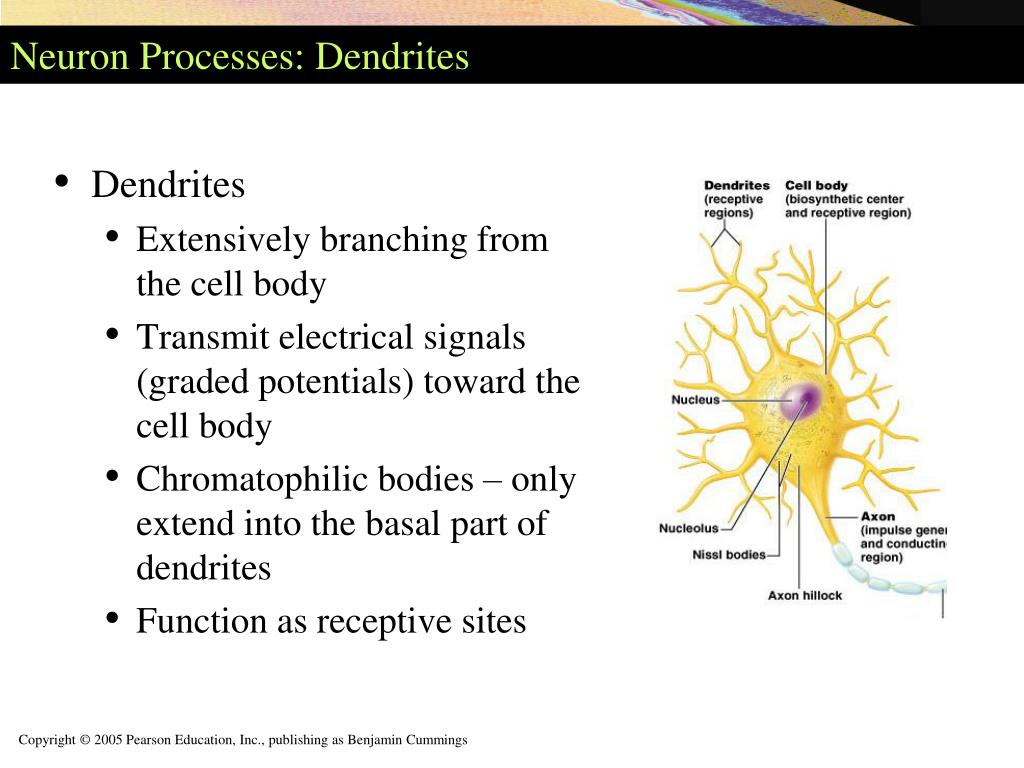
Such multifaceted approaches have further demonstrated the extent to which dendrite structure and function may undergo plastic changes that contribute to development, learning and neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disease. Dendrites play a central role in neuronal computation by integrating thousands of synaptic inputs to generate the output of the neuron in the form of. The research focused on the structure and function of dendrites, which are components of neurons, the nerve cells in the brain. Advances in molecular, electrophysiological and imaging techniques have led to a rapid enhancement in our understanding of the mechanisms that shape dendritic structure, function and connectivity and the contribution of dendritic computation to behavior. Dendrites play a central role in neuronal computation by integrating thousands of synaptic inputs to generate the output of the neuron in the form of axosomatic action potentials.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
